PRACTICE PAPER -3 CLASS : X SUBJECT: SCIENCE (only PHYSICS question shown here) (Based on Full Syllabus) M.M.: 80 DURATION: 3 HRS |
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper has five sections and 12 questions. All questions are compulsory. (iii) Section–A has 4 MCQs and 2 assertion-reason type of 1 mark each; Section–B has 1 questions of 2 marks each; and Section–C has 3 questions of 3 marks each; Section–D has 1 questions of 5 marks each; Section–E has 1 case based question of 4 marks. (iv) Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. (v) For case study questions in section E, there is one choice in one subpart, with 3 questions based per case study. |
SECTION A (MCQs)
| Q1 | In the following cases, a ray is incident on a concave mirror. In which case is the angle of incidence equal to zero? (a) A ray parallel to the principal axis. (b) A ray passing through the centre of curvature and incident obliquely. (c) A ray passing through the principal focus and incident obliquely. (d) A ray incident obliquely to the principal axis, at the pole of the mirror. |
Q2 | The Unit of potential difference may be expressed as (a) volt (b) Joule / coulomb (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of the above |
| Q3 | Two magnetic field lines:
|
| Q4 | Aditi is advised by his optician to wear spectacles with convex lenses. What type of defect of vision is he suffering from? |
Q5 to Q6 are assertion-reasoning based questions. These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate options given below: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (c) A is true but R is false. (d) A is false but R is true. |
| Q5 | Assertion (A): The near-point of a hypermetropic eye is more than 25 cm away. Reason (R): Hypermetropia is corrected using spectacles containing concave lenses. |
| Q6 | Assertion (A): The resistivity of a substance does not depend on the nature of the substance and temperature. Reason (R): The resistivity of a substance is a characteristic property of the material. |
SECTION B
Q7 to Q7 are very short answer questions
Q7 | If the speed of light in vacuum is \( 3\times 10^{8} \;ms^{-1}\),find the speed of light in a medium of absolute refractive index 1.5.ORA transparent medium A floats on another transparent medium B.When a ray of light travels obliquely from medium A to B, the refracted raybends away from the normal. Which of these two media is optically denser and why? |
SECTION C
Q8 to Q10 are short answer questions
Q8 | (a) Define the SI unit of potential difference.(b) What are mA and \(\mu\) A ? How are they related to ampere(A) ?(c) A charge of 20 C passes through a wire which is maintained at a potential difference of 5 V. Calculate the amount of work in moving the charge across the wire ? |
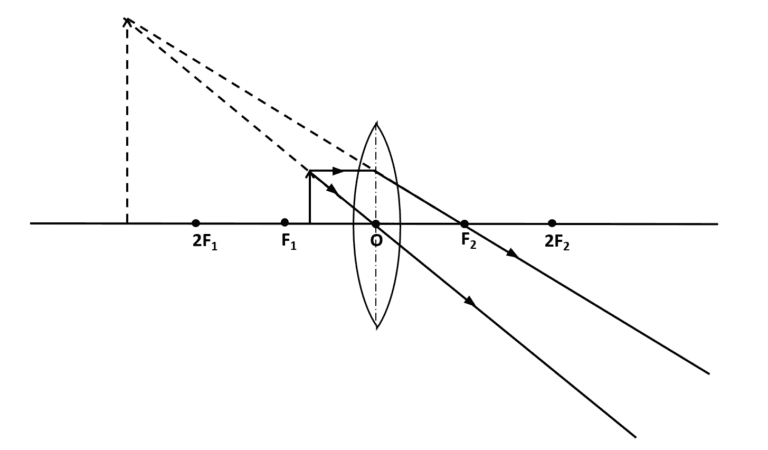
Q9 | The image of a candle flame formed by a lens is obtained on a screen placed on the other side of the lens.If the image is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm,at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens?What is the nature of the image and the focal length of the lens? |
Q10 | A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual image. Is this a correct statement?If yes, then specify the position of the object and draw a ray diagram to support your answer.ORAn object 5 cm in length is placed 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm.Find the position, nature and size of the image formed. |
SECTION D
Q11 to Q11 are long answer questions
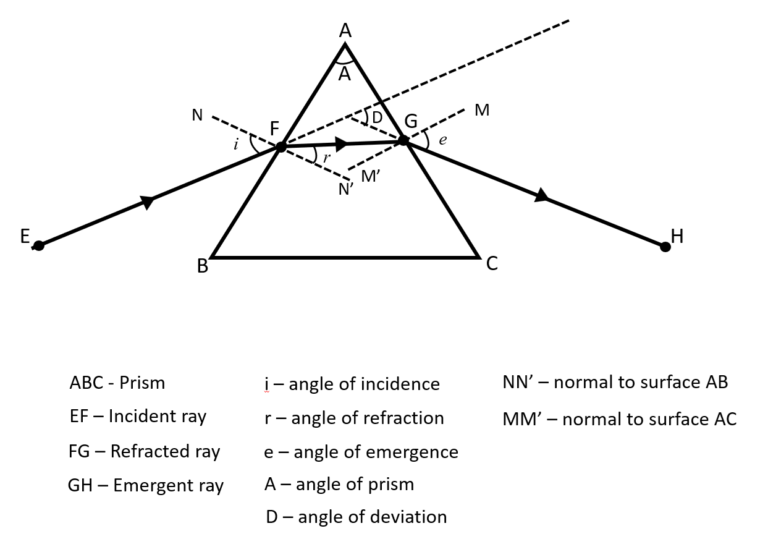
Q11 | Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using a labelled ray diagram. Mark the following in the diagram:A – Angle of prism,D – Angle of deviation,i – Incident angler – Angle of refraction,e – Emergent angleAlso label the Incident, Refracted and the Emergent raysDefine the angle of deviation. |
SECTION E
Q12 to Q12 are case-based / data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts.
Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts
Q12 | The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole. the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear-view mirror in automobiles because it can form an small and erect image of an object and thus covers a wider field of view.
(a) What is the position of the image when an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror? (1) (b) Why convex mirrors are preferred as a rear-view mirror in automobiles? (1) (c) A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a concave mirror and its sharp image is obtained on a plane sheet of paper. (i) What is the name given to the point where the sharp image is obtained? (1) (ii) Determine the radius of curvature, if the point where sharp image is obtained is 10 cm away from the pole of the mirror. (1) OR (c) A linear object of 5 cm size is placed normally at 2F of a concave mirror. What would be the size of its image ? What would be the nature of the image ? (2) |