PRACTICE PAPER -1 CLASS : X SUBJECT: SCIENCE ( Only Physics Questions shown here) (Based on Half Yearly Syllabus) M.M.: 80 DURATION: 3 HRS |
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper has five sections and 12 questions. All questions are compulsory. (iii) Section–A has 4 MCQs and 2 assertion-reason type of 1 mark each; Section–B has 1 questions of 2 marks each; and Section–C has 3 questions of 3 marks each; Section–D has 1 questions of 5 marks each; Section–E has 1 case based question of 4 marks. (iv) Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. (v) For case study questions in section E, there is one choice in one subpart, with 3 questions based per case study. |
SECTION A (MCQs)
| Q1 | A student studies that a convex mirror always forms a virtual image irrespective of its position. What causes the convex mirror to always form a virtual image? (a) because the reflected rays never intersect (b) because the reflected rays converge at a single point (c) because the incident rays always travel parallel to the principal axis (d) because the incident rays get absorbed in the mirror |
| Q2 | Reason behind advance sunrise and delayed sunset (a) atmospheric refraction (b) total internal reflection (c) dispersion (d) reflection |
| Q3 | The device which maintains potential difference in a circuit is – (a) ammeter (b) voltmeter (c) battery (d) resistor |
| Q4 | The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the red light (a) is scattered the most by smoke or fog. (b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog. (c) is absorbed the most by smoke or fog. (d) moves the fastest in air. |
Q5 to Q6 are assertion-reasoning based questions. These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate options given below: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (c) A is true but R is false. (d) A is false but R is true. |
Q5 | Assertion: In myopia defect of vision, light from a distant object arriving at the eye lens converges at a point in front of the retina. Reason: The eye lens is producing too much convergence in the incident beam. |
| Q6 | Assertion : A convex mirror is a diverging mirror. Reason : Incident rays parallel to the principal axis meet at a point on the principal axis after reflection from the convex mirror. |
SECTION B
Q7 to Q7 are very short answer questions
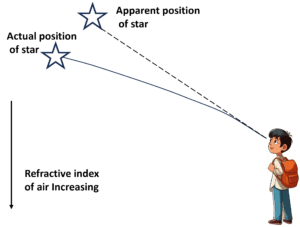
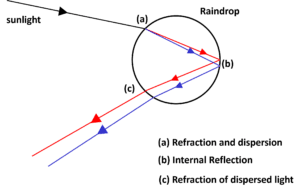
Q7 | (a) What is atmospheric refraction ? (b) Draw a well labelled diagram to show that the position of a star as seen by us is not its true position. OR (a) What is dispersion of white light? (b) Draw a well labelled diagram to show the formation of a rainbow. |
SECTION C
Q8 to 10 are short answer questions
Q8 | (a) Define the SI unit of electric current. (b) Potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is 3V. What is the meaning of this statement. (c) A current of 5 mA passes through the filament of a torch bulb. Determine the amount of electric charge passing through it in 5 minutes. |
Q9 | What is meant by the power of a lens ? Write its SI unit. A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of –20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens. |
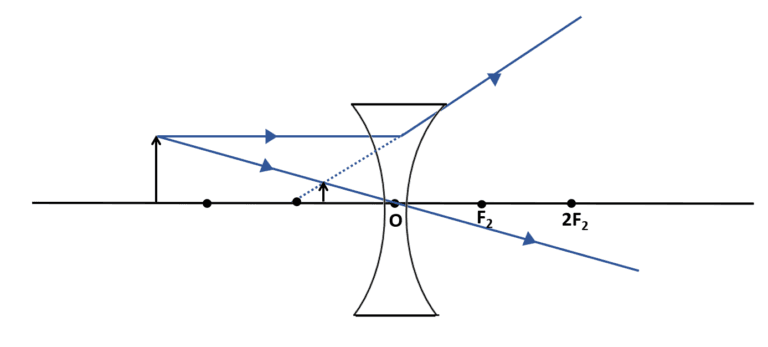
Q10 | A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm. The distance of the object from the mirror is 45 cm. Determine the position, nature and size of the image formed. OR An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. (i) Determine the distance of the image from the lens. What is the nature of the image obtained? (ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the position and nature of the image obtained in the above case. |
SECTION D
Q11 to 11 are long answer questions
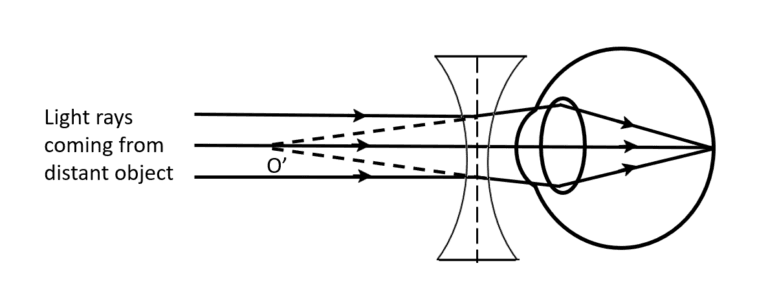
Q11 | (a) When do we consider a student sitting in the class to be myopic ? (b) List two causes of this defect. (c) Explain using a ray diagram how this defect of the eye can be corrected. (d) Why is the normal eye unable to focus on an object placed within 10 cm from the eye? |
SECTION E
Q12 to Q12 are case-based / data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts.
Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts
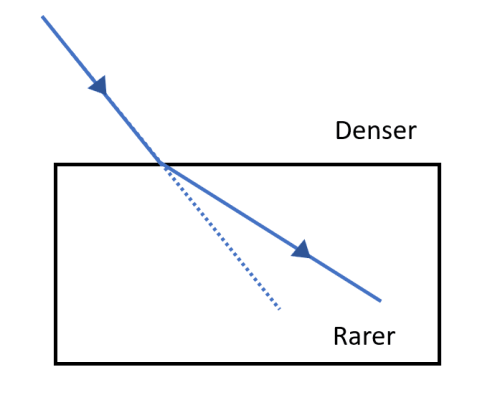
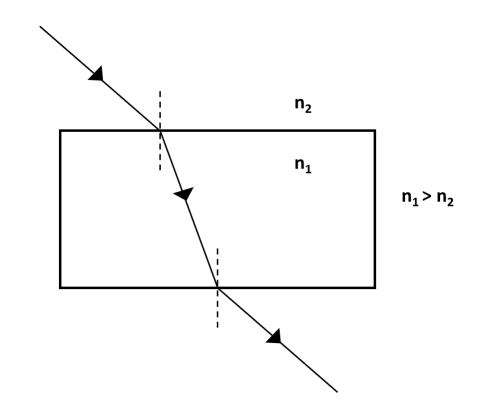
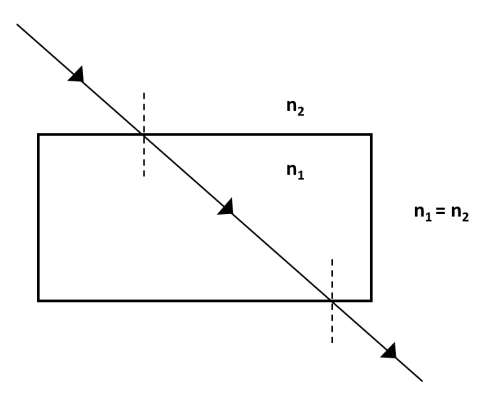
Q12 | When the rays of light travel from one transparent medium to another, the path of light is deviated. This phenomenon is called refraction of light. The bending of light depends on the optical density of the medium through which the light passes. The speed of light varies from medium to medium. A medium in which the speed of light is more is optically rarer whereas in which the speed of light is less is optically denser medium. Whenever light goes from one medium to another, the frequency of light does not change however, speed and wavelength change. It concluded that change in speed of light is the basic cause of refraction. (a) Refractive index of two material mediums X and Y are 1.3 and 1.5 respectively. In which of the two, the light would travel faster? (1) (b) Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a ray of light travelling from an optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium. (1) (c) State the two laws of refraction of light (2) OR (c) A glass slab made of material of refractive index \(n_{1}\) is kept in a medium of refractive index \(n_{2}\). A light ray is incident on the slab. Draw the path of the rays of light emerging from the glass slab if (i) \(n_{1}\) > \(n_{2}\) (ii) \(n_{1}\) = \(n_{2}\) |