Q1.
Magnification produced by a rear-view mirror fitted in vehicles is:
(a) less than one
(b) more than one
(c) equal to one
Q2.
If angle of incidence when a ray strikes a mirror is 30°, then find the angle that the reflected ray will make with the normal.
Q3.
Define principal focus of a concave mirror.
Q4.
Draw a diagram of a convex mirror and mark (i) pole, (ii) focus, (iii) centre of curvature, (iv) principal axis.
Q5.
What is the relation between radius of curvature and focal length of spherical mirror?
Q6.
A light ray parallel to the principal axis falls on a concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show the reflection by the concave mirror.
Q7.
Which mirror can give an erect and enlarged image of an object?
Q8.
What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a spherical mirror? How many rays can actually emerge from an object?
Q9.
Magnification of a spherical mirror is +2. Name the type of spherical mirror.
Q10.
What is the main advantage of using a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Q11.
Write the mirror’s formula.
Q12.
Define absolute refractive index.
Q13.
State Snell’s law.
Q14.
If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 ms-1, find the speed of light in a medium of absolute refractive index 1.5.
Q15.
Speed of light in water is 2.26 × 108 m/s and speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s. Which medium is optically denser?
Q16.
Write Len’s formula.
Q17.
Define power of a lens. What is its unit?
Q18.
Find the focal length of the lens of power – 2D. What type of lens is this?
Q19.
Assertion (A): For observing traffic at back, the driver mirror is convex mirror.
Reason (R): A convex mirror has much larger field of view than a plane mirror.
Q20.
Assertion (A): The height of an object is always considered positive.
Reason (R): An object is always placed above the principal axis in this upward direction.
Q21.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of Human eye.
Q22.
State the function of the following parts of human eye: (i) Iris and (ii) eye lens.
Q23.
What is hypermetropia? How can it be corrected? Explain with the help of ray diagrams.
Q24.
What is Presbyopia? How can it be corrected?
Q25.
What is cataract? How can it be corrected?
Q26.
Why do stars twinkle?
Q27.
Planets do not twinkle? Give reason.
Q28.
Show the path of a single ray of light through a glass slab with the help of a neat diagram.
Mark the following:
(i) Angle of incidence
(ii) Angle of refraction
(iii) Angle of emergence
(iv) Angle of Deviation
(v) Angle of Prism
Q29.
Draw a diagram to show dispersion of white light through a glass prism. For which colour is the refractive index of glass prism highest?
Q30.
How is a rainbow formed? Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a raindrop to explain the phenomenon.
Q31.
Draw a diagram to show the recombination of the 7 colours into white light using 2 prisms.
Q32.
What is meant by advanced sunrise and delayed sunset? What causes it?
Q33.
The position of the stars in the sky as it appears is their apparent position. Draw a diagram to show the actual and the apparent position of a star. Name the phenomenon that causes this.
Q34.
State the nature, position and magnification of the image formed in a human eye.
Q35.
Two lenses of power -1.75 D and +2.75 D are placed in contact. What will be the focal length of the combination?
Q36.
What are rods and cones? Where are they present?
Q37.
A person cannot see the fundamental colours (red, blue, green). What is this defect known as?
Q38.
The far point of a hypermetropic eye is 1.5m. Calculate the power of the lens that can be used to correct the defect. Name the type of lens used.
Q39.
A person cannot see beyond 60 cm. What defect of vision is he suffering from?
Calculate the power of the lens used to correct the defect. Name the type of lens.
Q40.
What will be the colour of scattered light when scattered by:
(i) Very fine particles
(ii) Large particles
(iii) Even larger particles
Q41.
Define one ampere of electric current.
Q42.
Name the device used to measure electric current in a circuit. How this device connected in a circuit?
Q43.
(a) 2 x 106µA = ……… A
(b) 2.4 x 10-3A = ………….. mA
Q44.
What is the conventional direction of electric current?
Q45.
A current of 0.1 A is withdrawn from a source for 2 minutes. Find the amount of electric charge flowing through the circuit.
Q46.
Draw a simple electric circuit consisting of a battery of 5V, a resistor of 2 ohms, an ammeter, a voltmeter, a plug key and connecting wires.
Q47.
Define electric potential difference.
Q48.
Potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is 10 V. What the meaning of this statement?
Q49.
Name the device which is used to
(a) measure potential difference
(b) maintain potential difference
Q50.
State Ohm’s law.
Q51.
Which of the graphs shown below represents the Ohm’s law?
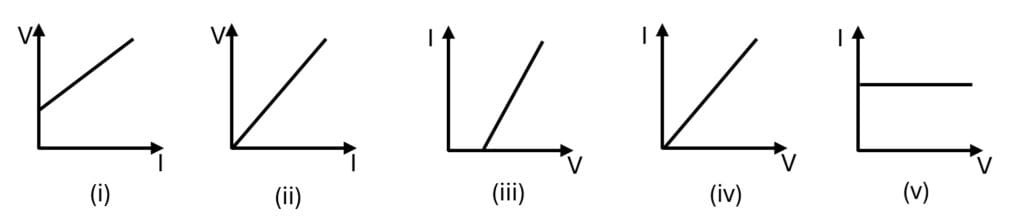
Q52.
Define the SI unit of resistance.
Q53.
State the factors on which resistance of a conductor depends upon.
Q54.
In the experiment to study the dependence of current (I) on the potential difference (V) across a resistor, a student obtained a graph as shown.
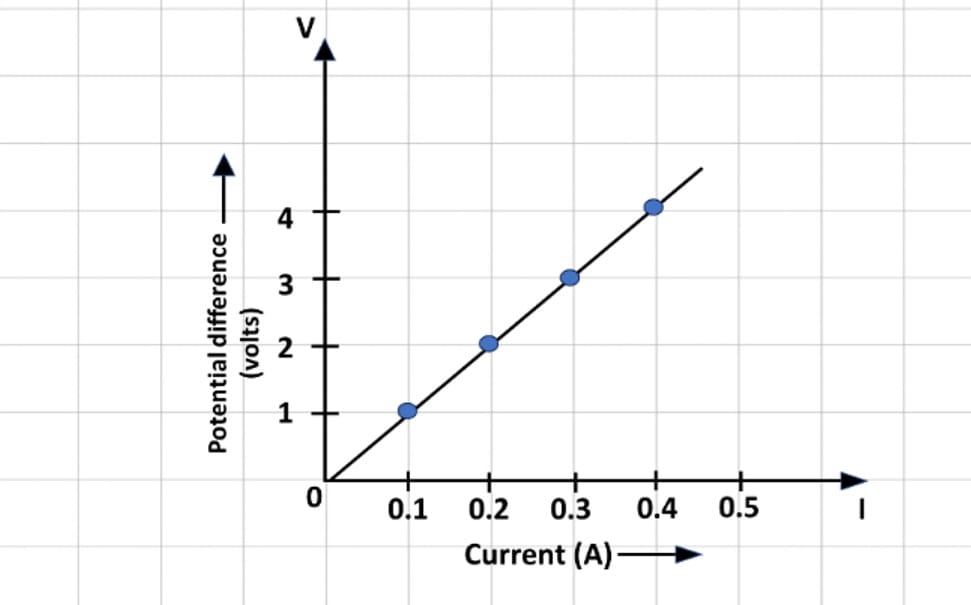
(i) What does the graph depict about the dependence of current on the potential difference?
(ii) Determine the resistance of the conductor from the above graph.
Q55.
List in tabular form the differences between ammeter and voltmeter.
Q56.
How will the resistivity of a conductor change if its length is doubled by stretching it?
Q57.
A copper wire of resistance 10 Ω is stretched to twice its length. Determine its new resistance.
Q58.
I-V graph for two wires A, B and C are shown in the figure. Arrange the wires in the increasing order of their resistance. Give justification for your answer.
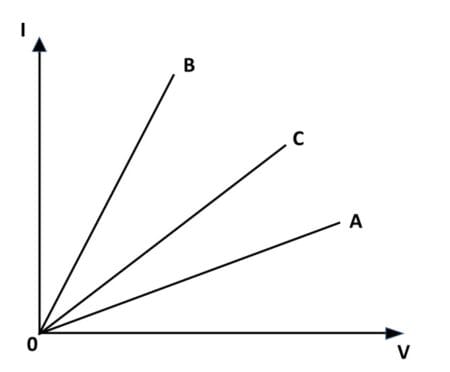
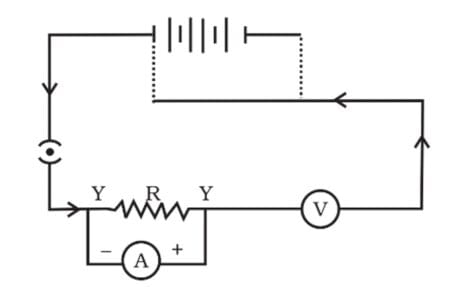
Q59.
A child has drawn the electric circuit to study Ohm’s law as shown in figure. His teacher said that the circuit diagram needs correction. Study the circuit diagram and redraw it after making all corrections.
Q60.
What does the given electric symbol in a circuit represent?
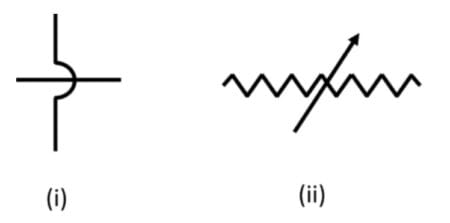
Q61.
How does a solenoid behave like a bar magnet? Show with the help of a diagram. Can you determine the north and south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Q62.
What are magnetic field lines? Justify the following statements
(a) Two magnetic field lines never intersect each other.
(b) Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
Q63.
How is the strength of magnetic field near a straight current carrying conductor
(i) Related to the strength of current in the conductor?
(ii) Is affected by changing the direction of flow of current in the conductor?
Q64.
Observe the figure given below and answer the following questions:
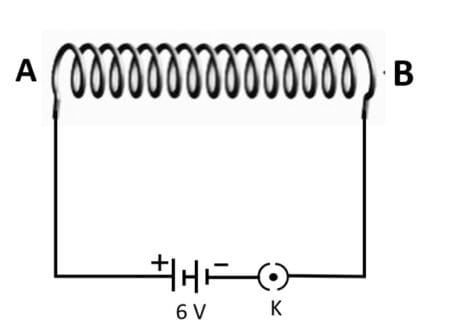
(a) Write the special name given to the coil AB which has many circular turns of insulated copper wire.
(b) State the nature of magnetic field inside AB when a current is passed through it.
(c) Redraw the diagram and sketch the pattern of magnetic field lines through and around AB.
(d) List two factors on which the strength of the magnetic field produced by AB depends.
(e) What is the effect of placing an iron core in the coil AB?
Q65.
List three sources of magnetic fields.
Q66.
Identify the poles of the magnet in the given figure (1) and (2).
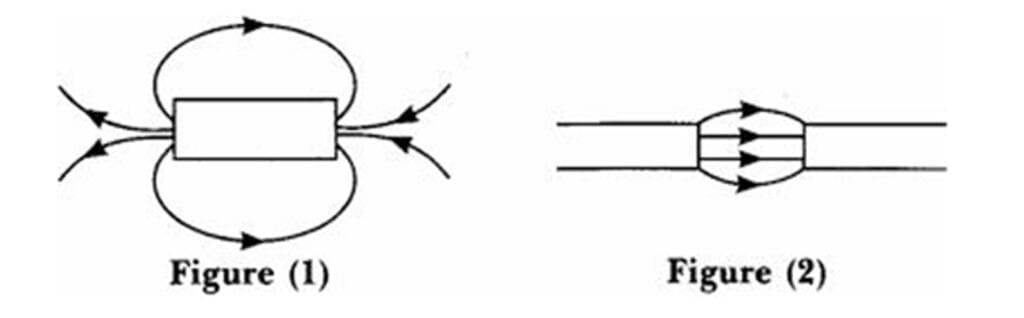
Q67.
How will the magnetic field produced at a point due to a current-carrying circular coil change if we:
(i) Increase the current flowing through the coil?
(ii) Reverse direction of current through the coil?
(iii) Increase the number of turns in the coil?
Q68.
What is the shape of a current carrying conductor whose magnetic field pattern resembles that of a bar-magnet?
Q69.
If the no. of turns of a circular current carrying coil is doubled, then how will the magnetic field produced by it changes?
Q70.
(a) Mention the factors on which the direction of force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field depend.
(b) Under what condition is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field maximum?
(c) A proton beam is moving along the direction of a magnetic field. What is force is acting on proton beam?
Q71.
State the rule to determine the direction of
(a) magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current.
(b) force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
Q72.
According to Fleming’s left hand rule, if the first finger points in the direction of ……….., the second finger in the direction of ……….., then the thumb will point in the direction of ……….. .
Q73.
Soft iron bar is inserted inside a current-carrying solenoid. The magnetic field inside the solenoid:
(a) Will decrease
(b) Will increase
(c) Will become zero
(d) Will remain the same
Q74.
A current carrying conductor is held in exactly vertical direction. In order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor when viewed from the top, the current should be passed in the conductor:
(a) From top to bottom
(b) From left to right
(c) rom bottom to top
(d) From right to left
Q75.
Current flows in a wire running between the S and N poles of a magnet lying horizontally as shown in the figure below:
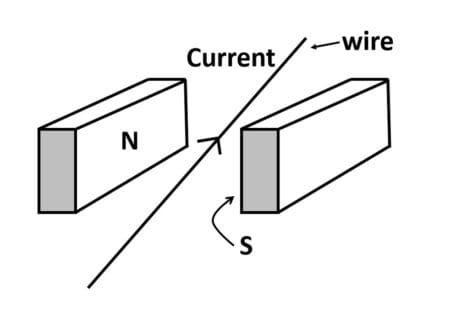
The force on the wire due to the magnet is directed:
(a) From N to S
(b) From S to N
(c) Vertically downwards
(d) Vertically upwards
Q76.
A current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field experiences a force. The displacement of the conductor in magnetic field can be increased by
(a) Decreasing the magnetic field.
(b) Decreasing the current in the conductor.
(c) Increasing the magnetic field.
(d) None of the above.
Q77.
A positively charged particle, say an alpha particle, projected towards west is deflected toward north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is
(a) Upward
(b) downward
(c) towards south
(d) towards east.
Q78.
When current is parallel to magnetic field, then force experience by the current carrying conductor placed in uniform magnetic field is
(a) Twice to that when angle is 60°
(b) Thrice to that when angle is 60°
(c) zero
(d) infinite
Q79.
Which of the following factors affect the strength of force experience by a current carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field?
(a) magnetic field strength
(b) magnitude of current in a conductor
(c) length of the conductor within magnetic field
(d) All of above
Q80.
A magnetic field directed in north direction acts on an electron moving in east direction. The magnetic force on the electron will act
(a) vertically upwards.
(b) towards the east.
(c) vertically downwards.
(d) towards the north
Q81.
Two bulbs of 120 W and 60 W are connected in series. The current through 120 W bulb is 1 A. Determine the current through the 60 W bulb.
(a) 1A
(b) 2A
(c) 0.5 A
(d) 0 A
Q82.
When white light enters a glass prism from the air, the angle of deviation is least for
(a) blue light
(b) yellow light
(c) violet light
(d) red light
Q83.
A person gets out in the sunlight from a dark room. How does his pupil regulate and control the light entering the eye?
(a) The size of the pupil will decrease, and less light will enter the eye
(b) The size of the pupil will decrease, and more light will enter the eye
(c) The size of the pupil will remain the same, but more light will enter the eye
(d) The size of the pupil will remain the same, but less light will enter the eye
Q84.
When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
(a) Crystalline lens
(b) The outer surface of the cornea
(c) Iris
(d) Pupil
Q85.
A person sees an object closer to his eyes. What changes will take place in his eyes?
(a) the pupil size will expand
(b) the ciliary muscles will contract
(c) the focal length of the eye lens will increase
(d) the light entering the eye will be more
Q86.
The image shows a light ray incident on a glass prism.
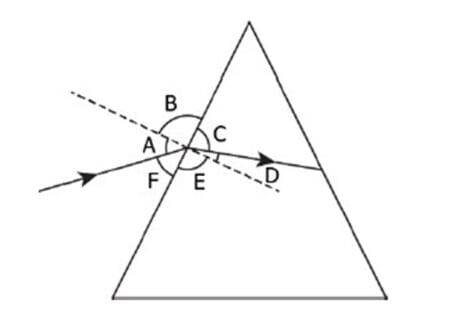
The various angles are labelled in the image. Which angle shows the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively?
(a) A and D
(b) C and F
(c) B and E
(d) D and F
Q87.
Which electrical component protects from short circuiting?
(a) Fuse
(b) Resistor
(c) Electric plug
(d) Switch
Q88.
The coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal, Because –
(a) Resistivity of an alloy (Nichrome) is generally higher than metal
(b) It has a high melting point.
(c) It does not oxidize/ burn, when it is red hot.
(d) All of above.
Q89.
B1, B2 and B3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in figure. When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by the ammeter A, what happens to the glow of the two bulbs when the bulb B1 gets fused?
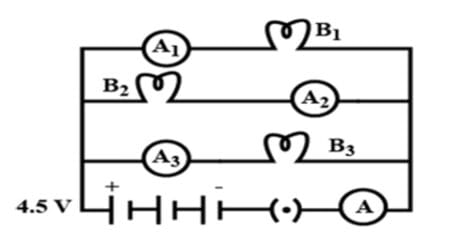
(a) Glow of the bulbs increased
(b) Glow of the bulbs Decreased
(c) Glow of the bulbs remains unchanged.
(d) None of above.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices
(A) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(B) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Q90.
Assertion: The connecting wires are made of copper.
Reason: Copper has very high electrical conductivity.
Q91.
Assertion: The total potential in system of resistors connected in series is equal to the sum of the individual’s potentials across each resistor.
Reason: The total current in system of resistors connected in parallel is equal to the sum of the individual’s currents moving through each resistor.
Q92.
Assertion: In domestic electric circuits, the wires in the supply, usually with red insulation cover, is called live wire (or positive)
Reason: Another wire, with black insulation, is called neutral wire (or negative)
Q93.
Assertion: When electric current is passed through a copper wire, magnetic needle kept near to wire shows deflection.
Reason: the electric current through copper wire has produced magnetic field.
Q94.
Assertion(A) : Alternating Current is used in household supply.
Reason (R) : AC electric power can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
Q95.
Assertion(A) : Light travels faster in glass than in air.
Reason (R) : Glass is denser than air.
Q96.
Assertion(A) : Refractive index has no units.
Reason (R) : The refractive index is a ratio of two similar quantities.
Q97.
Assertion: Blind spot is a small area of the retina which is insensitive to light where the optic nerve leaves the eye.
Reason: There are no rods or cones present at the junction of optic nerve and retina in the eye.
Q98.
Assertion: The near-point of a hypermetropic eye is more than 25 cm away.
Reason: Hypermetropia is corrected using spectacles containing concave lenses.
Q99.
Assertion: When a pencil is partly immersed in water and held obliquely to the surface, the pencil appears to bend at the water surface.
Reason: The apparent bending of the pencil is due to the refraction of light when it passes from water to air.
Q100.
Assertion: Myopia is the defect of vision in which a person cannot see the distant objects clearly.
Reason: This due to eye-ball being too short.