Q1.
An organism which can respond to ultrasound is
(a) Rhinoceroses
(b) whales
(c) elephants
(d) dolphins
Q2.
Why can’t we hear the scream of the bat?
(a) because its scream consists of infrasonic sound
(b) because its scream consists of ultrasonic sound
(c) because its scream is in audible range
(d) because its scream is having low amplitude and so low loudness.
Q3.
Note is a sound-
(a) of mixture of several frequencies
(b) of mixture of two frequencies only
(c) of a single frequency
(d) always unpleasant to listen
Q4.
The ceilings of concert halls and conference halls made curved. This is done –
(a) to make sound waves reaches all the part after reflection from the curved surface.
(b) to make the hall artistic and fancy.
(c) to reduce reverberation
(d) to prevent echo in hall
Q5.
When we change a low pitch sound to high pitch sound, we increase its
(a) frequency
(b) amplitude
(c) velocity
(d) wavelength
Q6.
Most television sets these days can be operated through a REMOTE CONTROL. How do most ‘remotes’ communicate with TV sets?
(a) Using radio waves
(b) Using infrared rays
(c) Using ultraviolet rays
(d) Using microwaves
Q7.
If the speed of the wave is 120 m/s and its frequency is 2000 Hz, then wavelength for this wave in cm will be:
(a) 6
(b) 0.6
(c) 60
(d) 600
Q8.
The persistence of sound in our brain is?
(a) 2 sec
(b) 344m/s
(c) 0.1s
(d) 0.2m/s
Q9.
Earthquake produces which kind of sound before the main shock wave begins
(a) ultrasound
(b) infrasound
(c) audible sound
(d) none of the above
Q10.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) A sound of single frequency is called a tone.
(b) The sound which is produced due to a mixture of several frequencies is called a note and is pleasant to listen to.
(c) A high pitch sound corresponds to more number of compressions and refractions passing a fixed point per unit time.
(d) The quality or timber of sound is that characteristic which enables us to distinguish one sound from another having the different pitch and loudness.
Q11.
(a) Give two applications of ultrasound. (one industrial and one medical application of ultrasound).
(b) Explain how defects in a metal block can be detected using ultrasound.
Q12.
Sounds of same loudness and pitch but produced by different musical instruments like a violin and flute are distinguishable.
Q13.
What is the range of frequencies associated with (a) infrasound (b) ultrasound?
Q14.
Name an organism which uses ultrasound for navigation.
Q15.
Which of the two graphs (a) and (b), shown below, representing the human voice is likely to be a male voice? Give reason for your answer.
Q16.
Why are the ceiling and wall behind the stage of good conference halls or concert halls made curved?
Q17.
A vibrating body produces sound. However, no sound is heard when a simple pendulum oscillates in air.
Q18.
Give two applications of multiple reflection of sound.
Q19.
State two conditions for hearing a distinct echo.
Q20.
An echo is returned in 3s. What is the distance of the reflecting surface from the source given that the speed of sound in air is 342 m/s?
Q21.
A child hears an echo from a cliff 4 seconds after the sound from a powerful cracker is produced. How far away is the cliff from the child, if the speed of sound is 340 m/s?
Q22.
What should be the minimum distance between the source of sound and obstacle to get an echo if the velocity of sound on a particular day is 330 m/s?
What will happen to this distance if the temperature of the day rises? Explain.
Q23.
Waves of frequency 100 Hz are produced in a string as shown in figure.
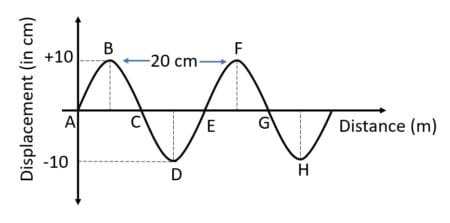
Give its: (a) Amplitude
(b) Wavelength
(c) Velocity
Q24.
Khushi, while visiting London, attended an opera performance. Its architecture and furnishings appealed her. The draperies, cushions, and curtains on the curved ceiling were all arranged correctly. Behind the stage, she noticed a soundboard. She was now curious as to whether each of these decorations was placed for the benefit of the hall’s aesthetics or for a scientific cause.

(a) In an opera house, what are the functions of curtains, pillows, and draperies?
(b) What are the benefits of the curved ceiling and soundboard?
(c) Loudhailers and horns are designed to send sound in a particular direction without spreading in all directions as shown in the given figures. Justify the above statement.
Q25.
A sound created in a big hall will persist by repeated reflection from the walls until it is reduced to a value where it is no longer audible. The repeated reflection that results in this persistence of sound is called reverberation. In an auditorium or big hall excessive reverberation is highly undesirable.
(a) What is reverberation?
(b) How reverberation can be reduced in a big hall? (any two ways)
(c) What is the difference between echo and reverberation?
(d) To hear a distinct echo the time interval between the original sound and the reflected sound must be at least
( a ) 1 s
(b) 0.1 s
(c) 0.5 s
(d) 2 s
Answer key for numericals