Q1.
Specify two conditions for magnitude of displacement to be equal to the distance travelled by an object. Also give a suitable example.
Q2.
A boy walks 10 m in straight path moving away from a lamp pole in a garden and walks 5m back on the same path. What is the displacement of the boy from the lamp pole?
Q3.
A car travels 5 km towards north than turns right and travels 3 km further, the car again turns right and travel 1 km and comes to rest. What is the distance travelled and displacement of the car?
Q4.
A particle is moving in a circular path of radius r.
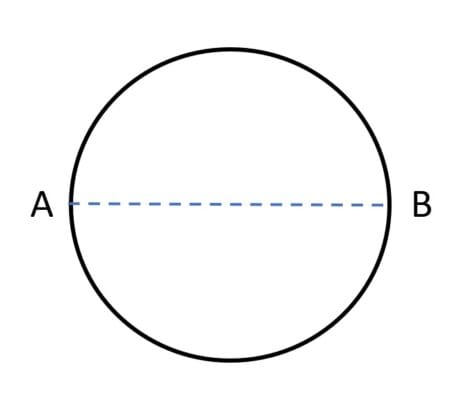
The displacement after half a circle would be:
(a) Zero (b) πr
(c) 2r (d) 2πr
Q5.
The numerical ratio of displacement to distance for a moving object is:
(a) Always less than 1
(b) Equal to 1 or less than 1
(c) Always more than 1
(d) Equal to 1 or more than one
Q6.
In which of the following cases of motions, the magnitude of the displacement may be zero ?
(i) If the car is moving on a straight road
(ii) If the car is moving in circular path
(iii) The pendulum is moving to and fro
(iv) The earth is moving around the sun
(a) only (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) only (i)
Q7.
Case based Questions
There are two towns Ramgarh and Arjangarh which are separated by a hill. The people of one town have to travel on a zigzag road which goes over the hill so as to reach the other town. Gaurav is a student of class IX in Ramgarh. Once Gaurav went from Ramgarh to Arjangarh on a scooter with his father. Driving at a constant speed of 50 km/h on the hilly road, it took exactly 30 minutes to reach Arjangarh. One day Gaurav told his father that if a straight tunnel could be dug through the hill, then it would become very easy for the people of two towns to visit each other. Keeping this in mind, Gaurav invited the people of both the towns and took a delegation to the Collector’s office. This delegation demanded the construction of a straight tunnel road through the hill. Gaurav explained the various advantages of connecting Ramgarh and Arjangarh through a tunnel road in the hill. The Collector liked the idea and a straight tunnel road was constructed after some time. One day Gaurav went from Ramgarh to Arjangarh through the straight tunnel road on the scooter with his father. Driving at a constant speed of 50 km/h, it took them just 12 minutes to reach Arjangarh. Both Gaurav and his father were very happy.
(1) What is the distance covered by Gaurav on going from Ramgarh to Arjangarh by travelling on road over the hill?
(a) 25 km (b) 10km
(c) 15km (d) 30km
(2) What is the distance covered by Gaurav on going from Ramgarh to Arjangarh by travelling on a straight tunnel road?
(a) 25km (b) 10km
(c) 15km (d) 30km
(3) How much less distance is to be covered now in going through the tunnel than on going over the hill?
(a) 10km (b) 15km
(c) 5km (d) 25km
(4) What is the displacement of Gaurav from Ramgarh on reaching Arjangarh on a straight tunnel road?
(a) 10km (b) 15km
(c) 5km (d) 25km