Q1.
Define one ampere of electric current.
Q2.
Name the device used to measure electric current in a circuit. How this device connected in a circuit?
Q3.
(a) 2 x 106µA = ……… A
(b) 2.4 x 10-3A = ………….. mA
Q4.
What is the conventional direction of electric current?
Q5.
A current of 0.1 A is withdrawn from a source for 2 minutes. Find the amount of electric charge flowing through the circuit.
Q6.
Draw a simple electric circuit consisting of a battery of 5V, a resistor of 2 ohms, an ammeter, a voltmeter, a plug key and connecting wires.
Q7.
Define electric potential difference.
Q8.
Potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is 10 V. What the meaning of this statement?
Q9.
Name the device which is used to
(a) measure potential difference
(b) maintain potential difference
Q10.
State Ohm’s law.
Q11.
Which of the graphs shown below represents the Ohm’s law.
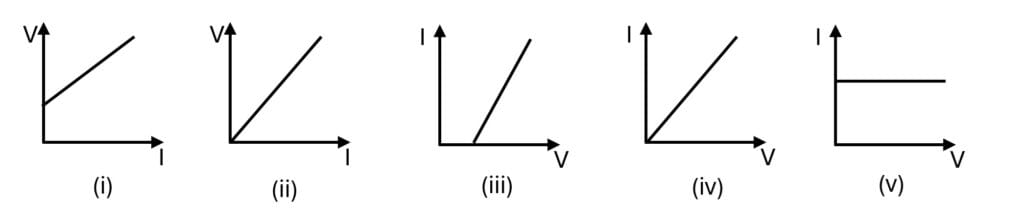
Q12.
Define the SI unit of resistance.
Q13.
State the factors on which resistance of a conductor depends upon.
Q14.
In the experiment to study the dependence of current (I) on the potential difference (V) across a resistor, a student obtained a graph as shown.
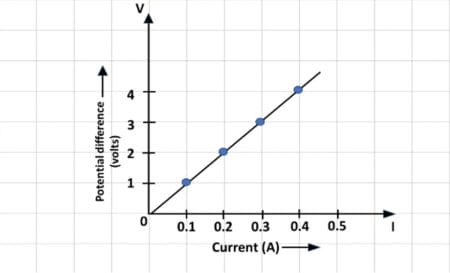
(i) What does the graph depict about the dependence of current on the potential difference?
(ii) Determine the resistance of the conductor from the above graph.
Q15.
List in tabular form the differences between ammeter and voltmeter.
Q16.
How will the resistivity of a conductor change if its length is doubled by stretching it?
Q17.
A copper wire of resistance 10 Ω is stretched to twice its length. Determine its new resistance.
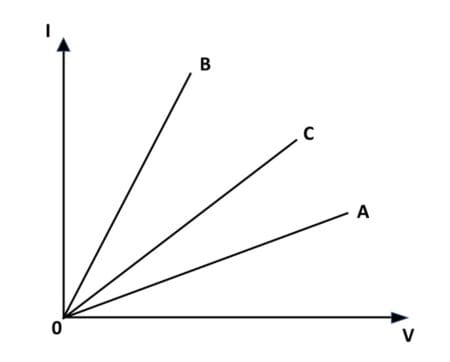
Q18.
I-V graph for two wires A, B and C are shown in the figure. Arrange the wires in the increasing order of their resistance. Give justification for your answer.
Q19.
A child has drawn the electric circuit to study Ohm’s law as shown in figure. His teacher said that the circuit diagram needs correction. Study the circuit diagram and redraw it after making all corrections.
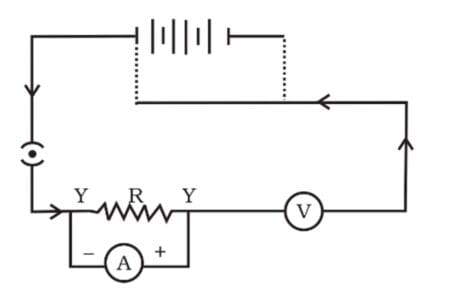
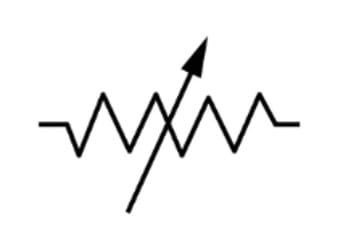
Q20.
What does the given electric symbol in a circuit represent?