Q1.
In which part of the human eye the image of an object is formed?
Q2.
Define accommodation.
Q3.
What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of the object from the eye?
Q4.
Name the part of the human eye responsible for the accommodation of eye lens.
Q5.
What is the value of near point and far point of:
(a) Myopic eye
(b) hypermetropic eye
(c) normal eye
Q6.
The image shows the ray diagram of a defected eye.
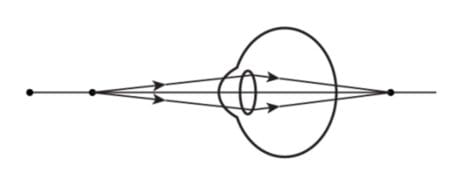
(a) Identify the defect of vision.
(b) Which lens should be used for the correction of the defect of the eye?
Q7.
A person went for a medical check-up and found that the curvature of his eye lens is increasing. Which defects he is likely to suffer from?
Q8.
Arun is standing at the bus stop. He can read his diary comfortably but cannot read the route number of the bus if it is beyond 5m. What type of lens should be used for correction of Arun’s eye defect?
Q9.
Write two causes of myopia.
Q10.
Write two causes of hypermetropia.
Q11.
Write two causes of presbyopia.
Q12.
Which colour of light is :
(i) scattered least by the particles of the atmosphere?
(ii) Scattered most by the particles of the atmosphere?
Q13.
Name three phenomenon involved in the formation of rainbow.
Q14.
Define angle of deviation.
Q15.
Danger signals are red in colour. Why?
Q16.
Colour of clear sky is blue. Why?
Q17.
Why does different colour get separated when white light passes through prism?
Q18.
When sunlight passes through a canopy of dense forest, its path becomes visible. Name the phenomenon.
Q19.
Assertion : Hypermetropia is the defect of eye in which only farther objects are seen.
Reason : Hypermetropia is corrected by using converging lens.
Q20.
Assertion – The sky looks dark and black instead of blue in outer space.
Reason – No atmosphere containing air in the outer space to scatter sunlight.