Q1.
On what basis is a chemical equation balanced?
Q2.
In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double that of gas collected over the other electrode?
Q3.
(a) What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead nitrate?
(b) Name the type of reaction.
(c) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above chemical reaction.
Q4.
What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating? Write a balanced chemical equation and three observations.
Q5.
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it? Write two observations.
Q6.
(a) A solution of substance ‘X’ is used for white washing. What is the substance ‘X’? State the chemical reaction of ‘X’ with water.
(b) How does this solution help in white washing?
Q7.
A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and a residue is left behind.
(i) Name the salt.
(ii) Write the equation for the decomposition reaction.
Q8.
On heating blue coloured powder of copper nitrate in boiling tube, a black colour substance X is obtained along with brown fumes of Y and a colourless gas Z.
(a) Identify X, Y and Z.
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(c) Identify the type of reaction.
Q9.
(a) Define the terms oxidation and reduction.
(b) Identify the substance that is oxidised and reduced in the following reaction.
(I) CuO(s) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + ZnO(s)
(II) MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Q10.
You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a china dish, the surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black colour substance.
(i) How has this black coloured substance formed?
(ii) What is that black substance?
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
(iv) How can we get copper back from its oxide.
Q11.
(a) What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride?
(b) State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction between them will not take place.
(c) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the type of reaction.
Q12.
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Q13.
Write one example for each of decomposition reaction carried out with help of
(i) Electricity
(ii) Heat
(iii) Light
Q14.
What type of chemical reactions take place when:
(a) Limestone is heated?
(b) A magnesium wire is burnt in the air?
(c) Electricity is passed through water?
(d) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride are mixed?
(e) Silver bromide is exposed to sunlight?
Q15.
When solid Ammonium Chloride and Barium Hydroxide are mixed in a clean and dry test tube, a gas having a pungent smell is liberated and water droplets are deposited on the outer surface of the test tube. Identify the type of reaction as endothermic or exothermic.
Q16.
Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction?
Q17.
A compound X is used in black and white photography. Identify X and write its chemical formula. Write a balanced chemical reaction when X is exposed to sunlight.
Q18.
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Q19.
What are precipitate reactions? Write any two examples.
Q20.
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Q21.
Write the equation and balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Q22.
(a) \( HNO_{3}+Ca(OH)_{2}\rightarrow Ca(NO_{3})_{2}+H_{2}O\)
(b) \(NaOH+H_{2}SO_{4}\rightarrow Na_{2}SO_{4}+H_{2}O\)
(c) \(NaCl+AgNO_{3}\to AgCl+NaNO_{3}\)
(d) \(BaCl_{2}+H_{2}SO_{4}\rightarrow BaSO_{4}+HCl\)
Q23.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
(a) Calcium hydroxide + carbon dioxide → calcium carbonate + water
(b) Zinc + silver nitrate → zinc nitrate + silver
(c) Aluminium + copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + copper
(d) Barium chloride + potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + potassium chloride
Q24.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Potassium bromide(aq) + barium iodide(aq) → potassium iodide(aq) + barium bromide (s)
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) → zinc oxide(s) + carbon dioxide(g)
(c) Hydrogen(g) + chlorine(g) → hydrogen chloride(g)
(d) Magnesium(s) + hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + hydrogen(g)
Q25.
Case Study
Double Displacement reactions are such types of chemical reactions in which two compounds react to form two new compounds. This happens mainly due to an exchange in the ions of the reactant compounds. For example, in the following reaction of Sodium Sulphate and Barium Chloride, we get two new products as Barium Sulphate and Sodium Chloride. This happens as the [Ba]²⁺ ions of Barium Chloride and [SO₄]²⁻ ions of Sodium Sulphate compound of the reactants are exchanged to give Barium Sulphate as white coloured precipitate.
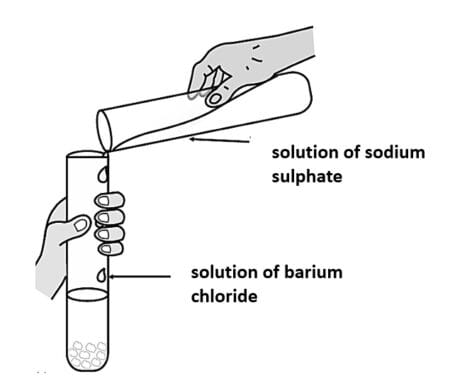
(a) The reaction shown results in the formation of a white coloured precipitate. What is precipitation?
(b) Complete the following double displacement reaction and write its balanced form.
\(BaCl_{2}(aq)+Al_{2}(SO_{4})_{3}(aq)\rightarrow\;?\)(c) When a solution of sodium chloride is added to silver nitrate solution, then a white precipitate of X is formed along with a solution of sodium nitrate. X is also known to be a compound used in black and white photography. Name the compound X that is formed in the reaction and mention what is the type of reaction it shows under the presence of sunlight.
(d) Balance the given double displacement reaction. Mention the colour and the name of the compound that is obtained as a precipitate.
Q26.
Which bases are called alkalies? Give an example of alkalies.
Q27.
Curd is not kept in copper and brass utensils. Why?
Q28.
Why does 1 M HCl solution have a higher concentration of H+ ions than 1 M CH3COOH solution?
Q29.
What happens when chlorine is passed over slaked lime at 313K? Write a chemical equation of the reaction involved and state two uses of the product obtained.
Q30.
(a) A white powder is added while baking bread and cakes to make them soft and fluffy. Write the name of the powder. Name its main ingredients. Explain the function of each ingredient.
(b) Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking.
Q31.
A gas ‘X’ reacts with lime water and forms a compound ‘Y’ which is used as a bleaching agent in the chemical industry. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’ Give the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Q32.
What is Plaster of Paris chemically? How is it prepared? List its two important uses.
Q33.
State reason for the following statements:
(i) Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not.
(ii) Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red whereas dilute hydrochloric acid does.
(iii) During summer season, a milk man usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(iv) For a dilution of acid, acid is added into water and not water into acid.
(v) Ammonia is a base but does not contain hydroxyl group.
Q34.
State the chemical properties on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid
(ii) as a soda acid fire extinguisher
(iii) to make bread and cake soft and spongy.
Q35.
What is observed when carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water
(i) for a short duration?
(ii) for a long duration? Also write the chemical equations for the reactions involved.
Q36.
Write the names of the product formed when zinc reacts with NaOH. Also write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved. Write a test to confirm the presence of the gas evolved during this reaction.
Q37.
What is the correct method for diluting concentrated acid? Describe the process.
Q38.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a basic salt”. Justify this statement. How is it converted into washing soda?
Q39.
List the important products of the Chlor-alkali process. Write one important use of each.
Q40.
Write name of the compound:
(a) Used for softening hard water.
(b) Used as an antacid.
(c) Which is a component of washing soda.
(d) Which is used as an oxidizing agent in many chemical industries?
Q41.
On burning Sulphur in oxygen, a colourless gas is produced.
(i) Write chemical equation for the reaction.
(ii) Name the gas formed.
(iii) State the nature of the gas.
(iv) What will be the action of this on a dry litmus paper?
Q42.
Design an experimental set-up to demonstrate that ‘‘Alcohol and glucose contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids’’. Also give the reason to justify this fact.
Q43.
Common salt is an important raw material for various chemicals of daily use. State in brief the method of preparation of
(i) Sodium hydroxide, and
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate from common salt.
Write balanced chemical equations of the reactions that occur.
Q44.
For making cake, baking powder is taken. If your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake at home.
(a) How will it affect the taste of the cake and why?
(b) How can baking soda be converted into baking powder?
(c) What is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda?
(d) Write the confirmatory test of the gas responsible for the sponginess of the cake.
Q45.
An acid ‘X’ present in tamarind when mixed with ‘Y’, produces a mixture ‘Z’. ‘Z’ on addition to a dough when heated makes cakes soft and spongy. Y’ is prepared from common salt and helps in faster cooking.
(i) Write the common names of ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’, and the chemical formula of Y.
(ii) How is ‘Y’ prepared and how does it help in making cakes soft and spongy? Illustrate the reaction with suitable chemical equation.
(iii) Write the name and chemical formula of a mild base other than Y’ used as an antacid.
Q46.
Write chemical equations to show what happens when an acid reacts with a
(i) metal
(ii) base and
(iii) carbonate
Write the name of the main product formed in each case.
Q47.
A person is feeling pain and irritation in the stomach due to indigestion. What could be the pH of the fluid in the stomach ? Write the common name of the medicines people use for remedy. Give the chemical name of ‘‘milk of magnesia’’ often used for this purpose.
Q48.
Assertion (A): The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is a highly exothermic reaction.
Reason(R): Water must always be added slowly to acid with constant stirring.
Q49.
Assertion (A) : All alkali are bases but not all bases are alkali.
Reason (R) : Alkali are the special kind of bases which dissolve in water without any reaction but not all bases possess that property.
Q50.
Assertion(A): Carbonic acid is a weak acid.
Reason(R): It ionizes completely in its aqueous solution.
Q51.
Zinc oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide. Give reason
Q52.
Why does calcium start floating when it reacts with water? Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
Q53.
By the transfer of electrons, illustrate the formation of bond in magnesium chloride and identify the ions present in this compound.
Q54.
An ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervescence. Name the type of ore with one example. What steps will be required to obtain metal from the enriched ore? Also write the chemical equations for the reactions involved in the process.
Q55.
How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore? Explain the various steps supported by chemical equations. Draw labelled diagram for the electrolytic refining of copper.
Q56.
Write chemical equations for the reactions taking place when:
(i) zinc sulphide is heated in air.
(ii) zinc carbonate is calcinated.
Q57.
Why do some metal surfaces acquire a dull appearance when they are exposed to moist air? Write colour acquired by the surfaces of copper and silver in such situation and also write the chemical names of the substances due to which it happens.
Q58.
How are alloys better than metals? Give composition of solder and amalgam.
Q59.
Give reason for the following:
(a) Ionic compounds have higher melting point and higher boiling point.
(b) Sodium is kept immersed in kerosene.
(c) Reaction of calcium with water is less violent.
(d) Silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air.
(e) Prior to reduction the metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted into metal oxides for extracting metals.
Q60.
How is sodium obtained from molten sodium chloride? Give all the equations of the reactions.
Q61.
Write two differences between calcination and roasting.
Q62.
What is a thermite reaction? How is it used to join the railway tracks or cracked machine parts?
Q63.
Write the electronic configurations of sodium and chlorine. Show the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine by the transfer of electrons.
Q64.
Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) Calcium with water
(b) Iron with steam
(c) Aluminium with steam
(d) Potassium with water
Q65.
Give reason for the following:
Hydrogen gas is not evolved when most of the metals react with nitric acid.
Q66.
State two reasons for the following facts:
(a) Sulphur is a non-metal. (b) Magnesium is a metal.
One of the two reasons must be supported with a chemical equation
Q67.
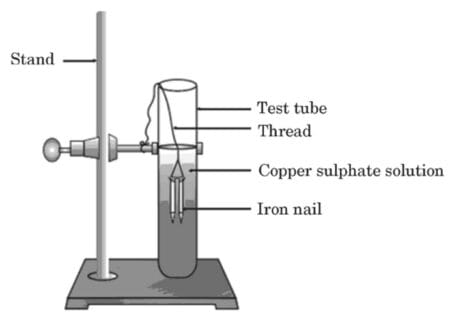
(a) Study the experimental set-up shown in the diagram and write chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved.
(b) Name and define the type of reaction.
(c) List two other metals which can be used in place of iron to show the same type of reaction with copper sulphate solution.
Q68.
(a) List any three observations which a student notes when a small piece of sodium metal is dropped in a beaker containing water.
(b) Write a test to identify the gas evolved (if any) during the reaction of these metals with water.
Q69.
Name one metal and one non-metal that exist in a liquid state at room temperature. Also, name two metals having a melting point less than 310 K (37°C)
Q70.
Which of the following oxides of iron would be obtained on the prolonged reaction of iron with steam?
(a) FeO
(b) Fe2O3
(c) Fe3O4
(d) Fe2O3 and Fe3O4
Q71.
Which of the following nonmetals is lustrous?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Sulphur
(c) Iodine
(d) Phosphorus
Q72.
The metal X does not react with cold water but floats on hot water with formation of colourless bubbles. Which of the following represents metal X.
(a) Aluminium
(b) Copper
(c) Magnesium
(d) Lead
Q73.
Divya cut pieces and compared the lustre of the freshly cut surfaces of the following metals:
aluminium, sodium, copper, iron
The freshly cut surface of which of these metals is likely to lose its lustre first on exposure to air?
(a) aluminium
(b) sodium
(c) copper
(d) iron
Q74.
Assertion (A): Sodium oxide is an amphoteric oxide.
Reason (R): Oxides which react with acids as well as bases are amphoteric oxides.
Q75.
Assertion(A): Anodising is a method to prevent metal from corrosion.
Reason(R): Anodising is a process of coating iron with a layer of zinc.
Q76.
What happens when ethanol is heated at 443 K with excess of conc. H2SO4?
Q77.
What are covalent compounds? List their three characteristic properties?
Q78.
Name the compound formed when ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of conc.H2SO4 Name this reaction and define it.
Q79.
Name the gas evolved when ethanoic acid is added to sodium carbonate. How would you prove the presence of this gas?
Q80.
What is the industrial application of hydrogenation?
Q81.
With the help of balanced chemical equations explain what happens when ethanol is heated with (i) alkaline solution of potassium permanganate, (ii) excess concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K.
Q82.
Mention any two uses of ethanol.
Q83.
Write a chemical equation in each case to represent the following types of chemical reactions of organic compounds: (i) Oxidation reactions ii) Addition reactions (iii) Substitution reactions.
Q84.
(a) Distinguish between esterification and saponification reactions of organic compounds with the help of the chemical equation for each.
(b) What is the use of esterification and saponification process?
Q85.
Which of the following are correct parts of micelle formation
(a) A=hydrophilic end, B= oil droplet, C= hydrophobic end
(b) A= hydrophobic end, B= hydrophilic end, C= oil droplet.
(c) A= oil droplet, B = hydrophilic end, C=hydrophobic end.
(d) A= oil droplet, B= hydrophobic end, C=hydrophilic end
Q86.
A gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and also write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Q87.
In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
The atomic number of chlorines are 17.
(a) Write its electronic configuration
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule.
Q88.
A salt X is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(a) Name the salt X and the gas evolved.
(b) Also, write chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Q89.
What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Q90.
Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which 6 carbon atoms are arranged in a ring.
Q91.
Micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water? State reason.
Q92.
How soap and detergent molecules differ chemically?
Q93.
Give a reason why soaps do not form lather in hard water?
Q94.
List two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
Q95.
Define homologous series. Write any two features of the series.
Q96.
Name the functional groups present in the following compounds:
(a) CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
(b) CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
Q97.
Name the organic compound prepared by Wohler from an inorganic compound called ammonium cyanate.
Q98.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following
(i) methane is heated in presence of Oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
(ii) Methane when reacted with chlorine in presence of sunlight.
Q99.
A carbon compound P has two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms.
(a) Is P a saturated or unsaturated carbon compound. Justify your answer by drawing the structural formula.
(b) On combustion will P burn with blue flame or yellow flame? Give reason for your answer
Q100.
Carbon forms large number of compounds due to:
(a) Catenation only
(b) Tetravalency only
(c) Both catenation and tetravalency
(d) None of the above